Cholesterol is related to but not the direct cause of arteriosclerosis, heart disease, and strokes. We cannot live without cholesterol, we must have it to make cell membranes, vitamin D, many hormones, and bile salts. Yet it is related to heart disease. In general, the higher the cholesterol the worse the risk for heart disease. But it is not the total that is most important, it is the relationship between types of cholesterol subfractions. There are nine different types of LDL cholesterol and five different types of HDL that provide even further information. In general, it is the ratio of HDL to total cholesterol that should be used in general screens. Lowering LDL has value to a certain point, but beyond a certain point low cholesterol may reduce heart disease but increase all cause mortality. Vytorin is a combination of Zocor and Zetia to lower cholesterol more may reduce mortality from heart disease, but overall survival is not increased, and all cause mortality may be higher.
 Dr. Len and Nurse Vicki present everything you need to know about cholesterol. What it is, what the fractions mean, what they predict, and what we can do to deal with elevated levels. Statins, how they work, what they do, and their side effects are reviewed. The role of inflammation, oxidized cholesterol, and why it should not be lowered too much are explained. The deception of big pharma is revealed in the Vytorin story. The causes of inflammation can be managed with lifestyle better than with drugs. HDL and LDL and their ratios are reviewed and contrasted. The role of supplements in lowering cholesterol is reviewed.
Dr. Len and Nurse Vicki present everything you need to know about cholesterol. What it is, what the fractions mean, what they predict, and what we can do to deal with elevated levels. Statins, how they work, what they do, and their side effects are reviewed. The role of inflammation, oxidized cholesterol, and why it should not be lowered too much are explained. The deception of big pharma is revealed in the Vytorin story. The causes of inflammation can be managed with lifestyle better than with drugs. HDL and LDL and their ratios are reviewed and contrasted. The role of supplements in lowering cholesterol is reviewed.
 For primary prevention of heart attacks there's no data showing that there's an increase in survival. And there are many side effects of statins that are problematic such as liver inflammation, peripheral neuropathy, muscle inflammation, kidney failure, global amnesia. Lifestyle is still the major way to stop and reverse heart disease. There is value during an acute heart attack and for secondary prevention of heart attacks.
For primary prevention of heart attacks there's no data showing that there's an increase in survival. And there are many side effects of statins that are problematic such as liver inflammation, peripheral neuropathy, muscle inflammation, kidney failure, global amnesia. Lifestyle is still the major way to stop and reverse heart disease. There is value during an acute heart attack and for secondary prevention of heart attacks. A new ultra-bad very sticky form of LDL cholesterol that is small and dense has been identified and found to be present in both type 2 diabetes and in the elderly. It may be the reason why the risk of heart attack and stroke is eleveated in these groups. The cause is suspected to be related to glycation (damage to proteins by high levels of glucose) and is more likely to occur when blood sugar levels are above 170, as these levels activate an enzyme called aldolase reductase that speeds the conversion of glucose to toxic sorbitol.
A new ultra-bad very sticky form of LDL cholesterol that is small and dense has been identified and found to be present in both type 2 diabetes and in the elderly. It may be the reason why the risk of heart attack and stroke is eleveated in these groups. The cause is suspected to be related to glycation (damage to proteins by high levels of glucose) and is more likely to occur when blood sugar levels are above 170, as these levels activate an enzyme called aldolase reductase that speeds the conversion of glucose to toxic sorbitol. The Framingham Study showed that for every rise of 1 mg/dL of HDL cholesterol, there was a 2% drop in the risk of an MI. However, not all HDL cholesterol is protective. HDL's protective effect depends on the environment in which it exists. In premenopausal women, generally HDL is protective. However, in postmenopausal women who have the metabolic syndrome and a chemical environment characterized by high triglycerides and inflammation, the HDL that forms is smaller and denser and does not participate in reverse cholesterol transport nearly as well. HDL is being asked to do a job it is no longer capable of doing.
The Framingham Study showed that for every rise of 1 mg/dL of HDL cholesterol, there was a 2% drop in the risk of an MI. However, not all HDL cholesterol is protective. HDL's protective effect depends on the environment in which it exists. In premenopausal women, generally HDL is protective. However, in postmenopausal women who have the metabolic syndrome and a chemical environment characterized by high triglycerides and inflammation, the HDL that forms is smaller and denser and does not participate in reverse cholesterol transport nearly as well. HDL is being asked to do a job it is no longer capable of doing.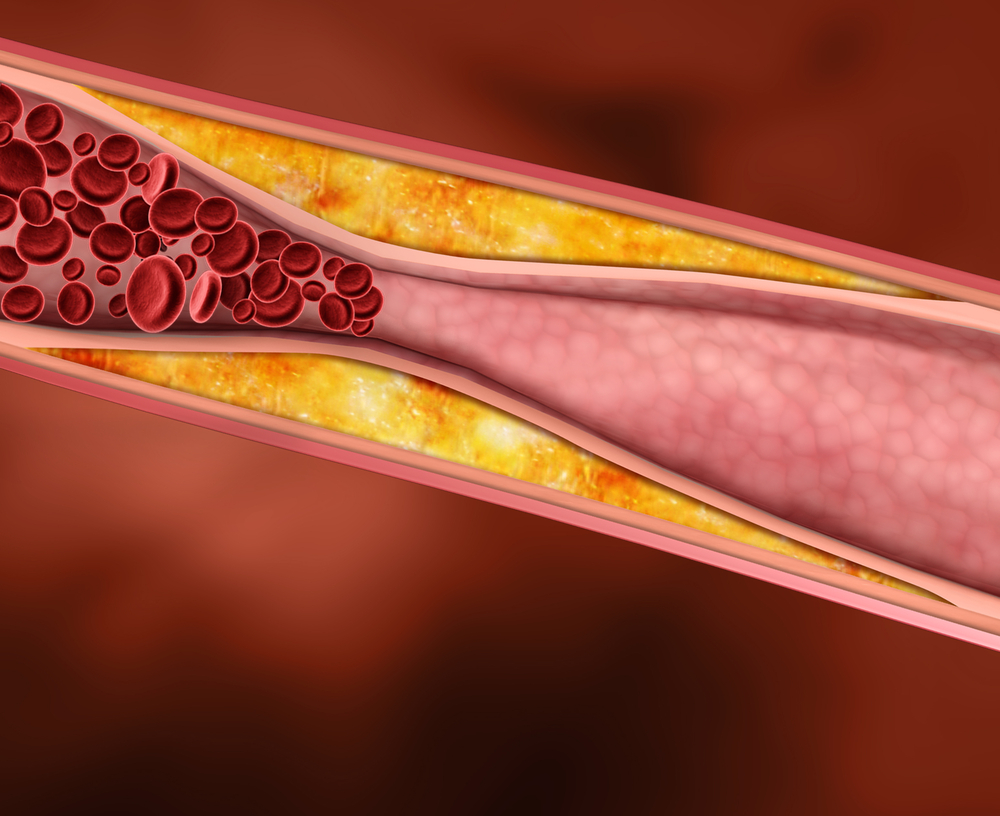 Apolipoprotein E (apoE) plays a major role in maintaining arterial softness by supressing production of a network of connective tissue in the body according to an article published in the November 2012 issue of Cell Reports. This work suggests that it may be the apoE-containing HDL that confers the main benefit of HDL cholesterol by promoting arterial softness. It is interesting that even when cholesterol is high the softening effects of apoE take precedence in protecting against heart attacks and strokes.
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) plays a major role in maintaining arterial softness by supressing production of a network of connective tissue in the body according to an article published in the November 2012 issue of Cell Reports. This work suggests that it may be the apoE-containing HDL that confers the main benefit of HDL cholesterol by promoting arterial softness. It is interesting that even when cholesterol is high the softening effects of apoE take precedence in protecting against heart attacks and strokes.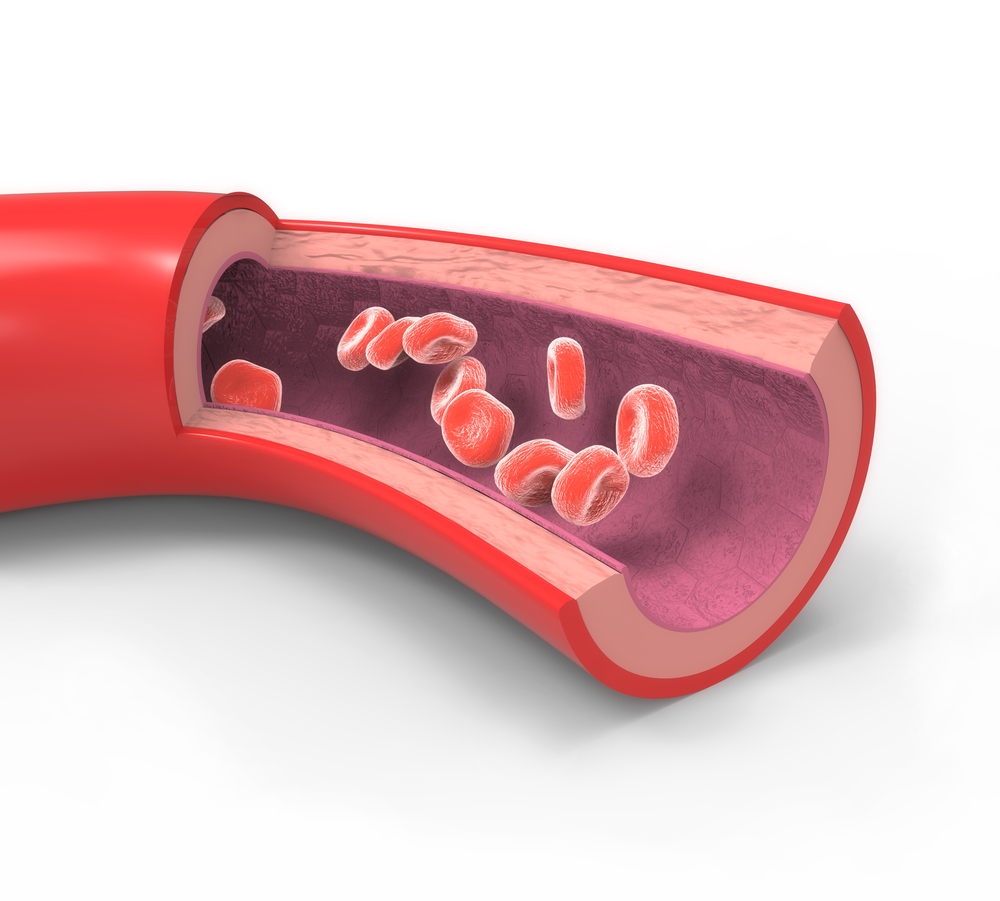 Treatment to increase HDL cholesterol has been viewed as useful, but new data published in the journal Lancet in May of 2012, suggests that there's no value in doing so to prevent heart attacks. It could be that HDL is a marker for increased risk for heart attack, much like the PSA is a marker for prostate cancer. This does not mean that statin drugs don't benefit people with established heart disease because LDL lowering is directly related to decrease the risk of MI and death in this setting.
Treatment to increase HDL cholesterol has been viewed as useful, but new data published in the journal Lancet in May of 2012, suggests that there's no value in doing so to prevent heart attacks. It could be that HDL is a marker for increased risk for heart attack, much like the PSA is a marker for prostate cancer. This does not mean that statin drugs don't benefit people with established heart disease because LDL lowering is directly related to decrease the risk of MI and death in this setting.




